Animal husbandry can be an excellent form of income for small- to large-scale farmers. The consumption of animal products has many benefits but potential risks attached to it too. The risks affect animals, farmers, and consumers. But how does animal husbandry relate to the overall health of humans, specifically?
Animal husbandry affects human health on several levels, including physical, mental, emotional, and socio-economic well-being. It can impact these spheres of human health indirectly or directly and positively or negatively, depending on the circumstances.
This article only touches the tip of the iceberg regarding the correlations between animal husbandry and human health. Numerous studies and research consider the health of humans and livestock in greater depth and provide lots of statistical data. The findings could be encouraging or terrifying, depending on the researcher's stance. First, however, let's start with the good news.
The Benefits Of Animal Husbandry Related To Human Health

When considering how animal husbandry relates to humans, there are obvious benefits to human health that can be considered. The various aspects of human health in this regard are discussed next, as well as the socio-economic benefits of animal husbandry to human health.
Health Benefits
Animal husbandry can benefit human health in a few ways. For example, the nutrients found in some animal products aid physical and cognitive development in humans and can improve their emotional health too.
Physical Health
On a physiological level, animal husbandry can improve the health of humans due to the nutrients found in animal products. But, of course, this is a contentious issue for strict vegans who believe these nutrients can be found in plants, and we acknowledge this stance.
- Animal products are a source of protein, fats, and minerals. The amino acids from proteins help to build and repair cells throughout the body.
- Animal fat, in moderation, can benefit human health. This is because many vitamins and minerals are fat-soluble, meaning they can't be absorbed into the body without a lipid. The fat-soluble vitamins are A, D, E, and K.
- Iron, calcium, sodium, magnesium, potassium, zinc, and selenium are some minerals found in animal products. Humans need these minerals in small doses for overall physical function and health.
Mental And Cognitive Health
Since animal products are a source of protein, fat, and minerals, they can benefit humans' mental and cognitive health. When a person's brain has all the nutrients it needs, it can function optimally, i.e., transmitting impulses through synapses more readily.
However, deficiencies in any of these nutrients can impede brain development and the regeneration of cells. As such, cognitive function can be impaired, for example, the inability to think clearly.
Emotional Health
Animal husbandry can affect the emotional health of humans both positively and negatively. For example, research has shown that human-animal interaction can decrease stress-related hormone (cortisol) levels in humans. Additionally, this interaction can lower blood pressure, boost mood, increase the feeling of social support, and reduce loneliness.
However, it is worth mentioning that these findings are more applicable to smaller-scale farmers who see their livestock more as pets than as a means to an end. For many large-scale farmers, the relationship between animal husbandry and emotional well-being is often negative.
Socio-Economic Benefits
People usually farm with animals to sell animal products or animal by-products. It is their income, and when business is doing well, the farmer should benefit financially and in other respects. In many African countries, owning livestock is a sign of wealth. For example, the more cattle a person has, the richer they are.
In these communities, cattle are used for payment, bartering, and sometimes income. For instance, livestock is used for "lobola," a "bride price" for taking on a new wife. The groom or his family pays lobola to the bride's parents.
In some areas, people barter using their livestock or animal products to get a service or product. For example, a dozen eggs could be bartered with a greengrocer for fresh produce.
The Drawbacks Of Animal Husbandry Related To Human Health
As beneficial as animal husbandry can be to human health, it can be detrimental, too. Animals can and do carry diseases and parasites that can have a mild to severe impact on human health.
Drawbacks That Affect Human Health
According to a study published in 2015, animal husbandry there is a strong link between animal husbandry and many human diseases. The diseases can be transmitted via infectious pathogens, animal-source food, and animal products.
Zoonotic Pathogens
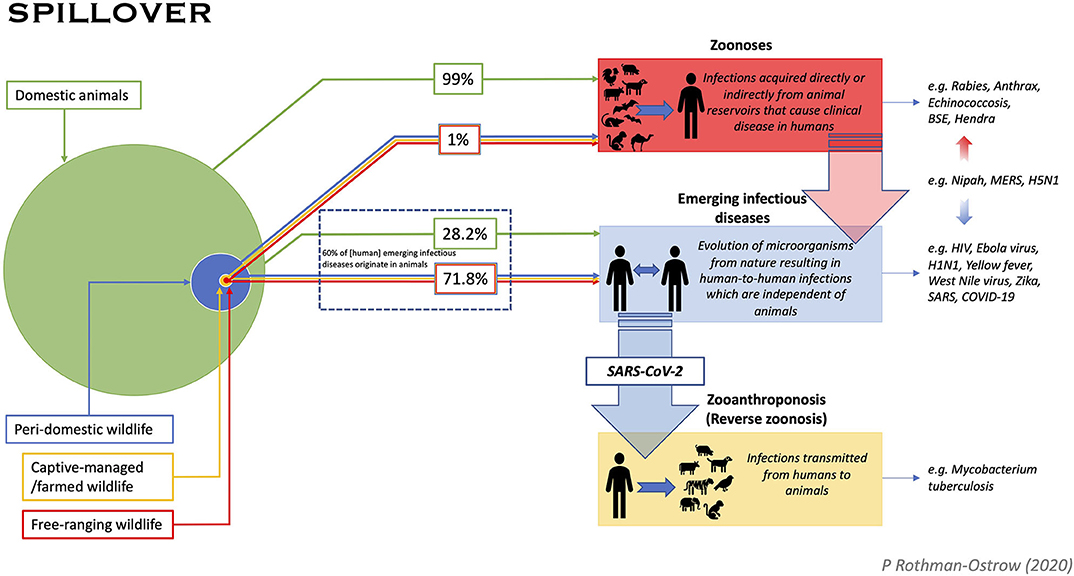
One of the risks of keeping livestock is the transmission of zoonotic pathogens from livestock to humans. Unfortunately, these pathogens are often neglected and can result in an outbreak among humans. The Coronavirus pandemic that escalated in 2019 is a vivid example of the transmission of a zoonotic pathogen from animals to humans.
However, COVID-19 doesn't fit into the World Health Organization's (WHO) of zoonoses, so it might be better to classify it as an "emerging infectious disease (EID) of probable animal origin."
Other zoonotic pathogens transmitted to humans include the following:
- Leptospirosis,
- Rabies,
- Anthrax,
- Q-fever,
- Cryptosporidium, and
- Trypanosomiasis.
Food-Borne Diseases
Food-borne diseases result from eating animal products or by-products infected by parasites. For example, Cysticercosis is an infection caused by swallowing the eggs of tapeworms. For example, the eggs of Taenia solium develop into cysts and infect human muscle and brain tissue. If cysts form in the brain, this infection is called neurocysticercosis.
According to WHO, neurocysticercosis is believed to be the cause of 30% of epilepsy development worldwide.
Common food-borne diseases that can have severe or fatal side effects are caused by bacteria like Salmonella, Escherichia coli (E-Coli), and Campylobacter. The most common food products that can cause Salmonellosis are poultry and eggs. Still, the bacteria can be found in other animal products.
Other food-borne diseases include taeniasis (from consuming undercooked pork or beef), cryptosporidiosis (nicknamed "Crypto,") and brucellosis.
The Development Of Antimicrobial Resistance
In animal husbandry, antibiotics are often used as a non-therapeutic measure to protect livestock from diseases. This is especially true in intensified farming practices where a whole herd or flock can be wiped out due to an ancient infectious disease. Interestingly, 80% of all antibiotics produced in the USA are sold for anti-therapeutic use for farm animals.
However, when humans consume animal products that have been treated by antibiotics or antimicrobials, they start to develop a resistance to such medications. Being resistant to antibiotics limits treatment options for humans when they need it most.
One example of antibiotic-resistant human infection is the "superbug" methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Chronic Diseases
Many chronic diseases in humans are attributed to the excessive consumption of certain animal products. The products in question usually contain energy-dense, high-level saturated fats. As a result, they can lead to the development of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Socio-Economic Drawbacks
The negative socio-economic aspects of animal husbandry can influence a person's health in many ways. For example, a farmer with livestock in a drought-stricken area might spend a lot of money trying to keep his stock alive. Going into debt to keep animals fed and watered can be highly stressful, especially if there is no end in sight.
Additionally, when fodder, medical, or oil prices soar, it can negatively impact a farmer's ability to farm and care for his animals efficiently. Operating costs may well outweigh the return, putting a farmer in the position to make difficult decisions, e.g., culling, prioritizing, downscaling, etc.
Conclusion
Animal husbandry can affect human health positively and negatively, directly and indirectly. The benefits of animal husbandry are mainly due to the nutritional values gained from consuming animal products and financial gain. However, animal husbandry carries risks to human health, particularly in transmitting infectious diseases and parasites.
Disclaimer: This is not a Veterinarian or Medical Advice
The information provided in this article should not be considered as veterinary or medical advice. The information provided here is for general educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional veterinary or medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. The reader should always consult their own veterinarian or medical professional for specific advice or treatment for their pet or personal health needs. Reliance on any information provided in this text is solely at the reader's own risk. The authors, publishers, and distributors of this text cannot be held responsible for any adverse effects or consequences resulting from the use or misuse of any information contained within.